Quest for the right Drug
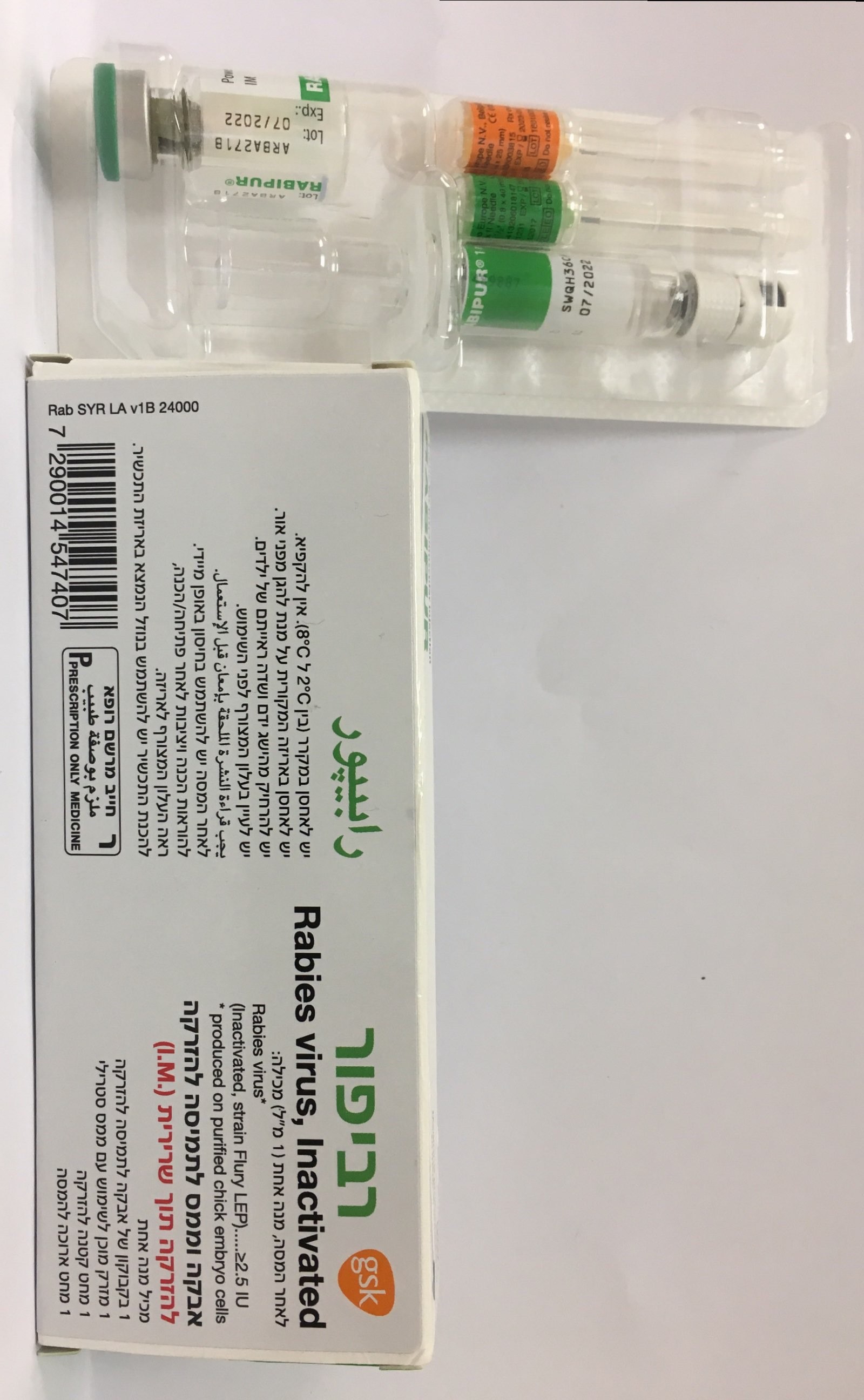
רביפור RABIPUR (RABIES, INACTIVATED, WHOLE VIRUS)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-שרירי : I.M
צורת מינון:
אבקה וממס להכנת תמיסה להזרקה : POWDER AND SOLVENT FOR SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Posology : מינונים
4.2 Posology and method of administration Posology The recommended dose for both primary immunization and boosters is 1.0 ml 1 Pre-exposure prophylaxis Primary immunization In previously unvaccinated individuals, three doses should be administered according to the conventional or rapid regimen as shown in Table 1. Table 1 Primary immunization regimens Conventional regimen Rapid regimen* st 1 dose Day 0 Day 0 2nd dose Day 7 Day 3 3rd dose Day 21 (or 28) Day 7 The conventional regimen of days 0,7,21 (or 28) is the preferable regimen. *The rapid regimen should only be considered for adults aged 18-65 years not able to complete the conventional pre-exposure prophylaxis regimen within 21 or 28 days before protection is required. Booster doses Booster doses are generally recommended every 2-5 years. Timing for booster after vaccination with rapid regimen has not yet been established (see also section 5.1). Serological testing for the presence of antibody ≥ 0.5 IU/ml to assess the need for booster doses should be conducted in accordance with official recommendations. Rabipur may be used to boost individuals previously immunized with any human diploid cell rabies vaccine. Post-exposure prophylaxis Post-exposure prophylaxis should commence as soon as possible after exposure. Table 2 summarises recommendations for post-exposure prophylaxis, including immunization, according to the type of exposure. Table 2: Recommended post-exposure prophylaxis according to type of exposure Category Type of exposure to a domestic or Recommended post-exposure of wilda) animal suspected or confirmed to prophylaxis exposure be rabid, or animal unavailable for testing I Touching or feeding animals None, if reliable case history is available. Licks on intact skin Contact of intact skin with secretions or excretions of a rabid animal or human case II Nibbling of uncovered skin Administer vaccine immediately b) Minor scratches or abrasions without Stop treatment if animal remains healthy bleeding throughout an observation period of 10 days c) or is proven to be negative for rabies by a reliable laboratory using appropriate diagnostic techniques. III Single or multiple transdermal bites d) or Administer rabies vaccine immediately, scratches, licks on broken skin. and rabies immunoglobulin, preferably as Rabipur_Vial_PFS_SPC_V4.1_Update_09-2019 Page 2 of 12 Contamination of mucous membrane with soon as possible after initiation of post- saliva (i.e. licks). Exposure to bats e). exposure prophylaxis. Rabies immunoglobulin can be injected up to 7 days after first vaccine dose administration. Stop treatment if animal remains healthy throughout an observation period of 10 days or is proven to be negative for rabies by reliable laboratory using appropriate diagnostic techniques a) Exposure to rodents, rabbits or hares does not routinely require rabies post-exposure prophylaxis. b) If an apparently healthy dog or cat in, or from a low-risk area is placed under observation, treatment may be delayed. c) This observation period applies only to dogs and cats. Except for threatened or endangered species, other domestic and wild animals suspected of being rabid should be euthanized and their tissues examined for the presence of rabies antigen by appropriate laboratory techniques. d) Bites especially on the head, neck, face, hands and genitals are category III exposures because of the rich innervation of these areas. e) Post-exposure prophylaxis should be considered when contact between a human and a bat has occurred, unless the exposed person can rule out a bite or scratch or exposure of a mucous membrane. In post-exposure prophylaxis of previously unvaccinated individuals, the vaccine should be administered according to Table 3. Table 3: Post-exposure immunization regimens for previously unvaccinated individuals Essen regimen Zagreb regimen Reduced Essen (5 doses) (4 doses) regimen (4 doses)2 1st dose Day 0 Day 0, 2 doses1 Day 0 2nd dose Day 3 Day 3 3rd dose Day 7 Day 7 Day 7 4th dose Day 14 Day 21 Day 14 5th dose Day 28 • 1 one injection in each of the two deltoids or thigh sites 2 this shortened Essen regimen may be used as an alternative for healthy, immunocompetent individuals provided they receive wound care plus rabies immunoglobulin in category III as well as in category II exposures and a WHO- prequalified rabies vaccine In previously vaccinated individuals, post-exposure prophylaxis consists of two doses administered on days 0 and 3. Rabies immunoglobulin is not indicated in such cases. In immunocompromised individuals with category II and III exposures, 5 doses should be given in combination with comprehensive wound management and local infiltration of rabies immunoglobulin as shown in Table 4. Table 4: Post-exposure immunization regimens for immunocompromised individuals Essen regimen Alternative to Essen 1st dose Day 0 Day 0, 2 doses1 2nd dose Day 3 Day 3 3rd dose Day 7 Day 7 Rabipur_Vial_PFS_SPC_V4.1_Update_09-2019 Page 3 of 12 4th dose Day 14 Day 14 5th dose Day 28 Day 28 1 Two doses of vaccine may be given on day 0, that is, a single dose of 1.0 ml vaccine should be injected into the right deltoid and another single dose into the left deltoid muscle. In small children, one dose should be given into the anterolateral region of each thigh. This would result in a total of 6 doses. When feasible, the rabies virus neutralising antibody response should be measured 2 to 4 weeks (preferably on day 14) following the start of vaccination to assess the possible need for an additional dose of the vaccine. Immunosuppressive agents should not be administered during postexposure therapy unless essential for the treatment of other conditions (see section 4.5). Paediatric population Paediatric individuals receive the same dose as adults (1.0 ml). Method of administration Rabipur is for intramuscular administration only. For adults and children ≥ 2 years of age, the vaccine should be administered into the deltoid muscle. For children < 2 years, the anterolateral area of the thigh is recommended. For instructions on reconstitution of the vaccine before administration, see section 6.6.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
