Quest for the right Drug
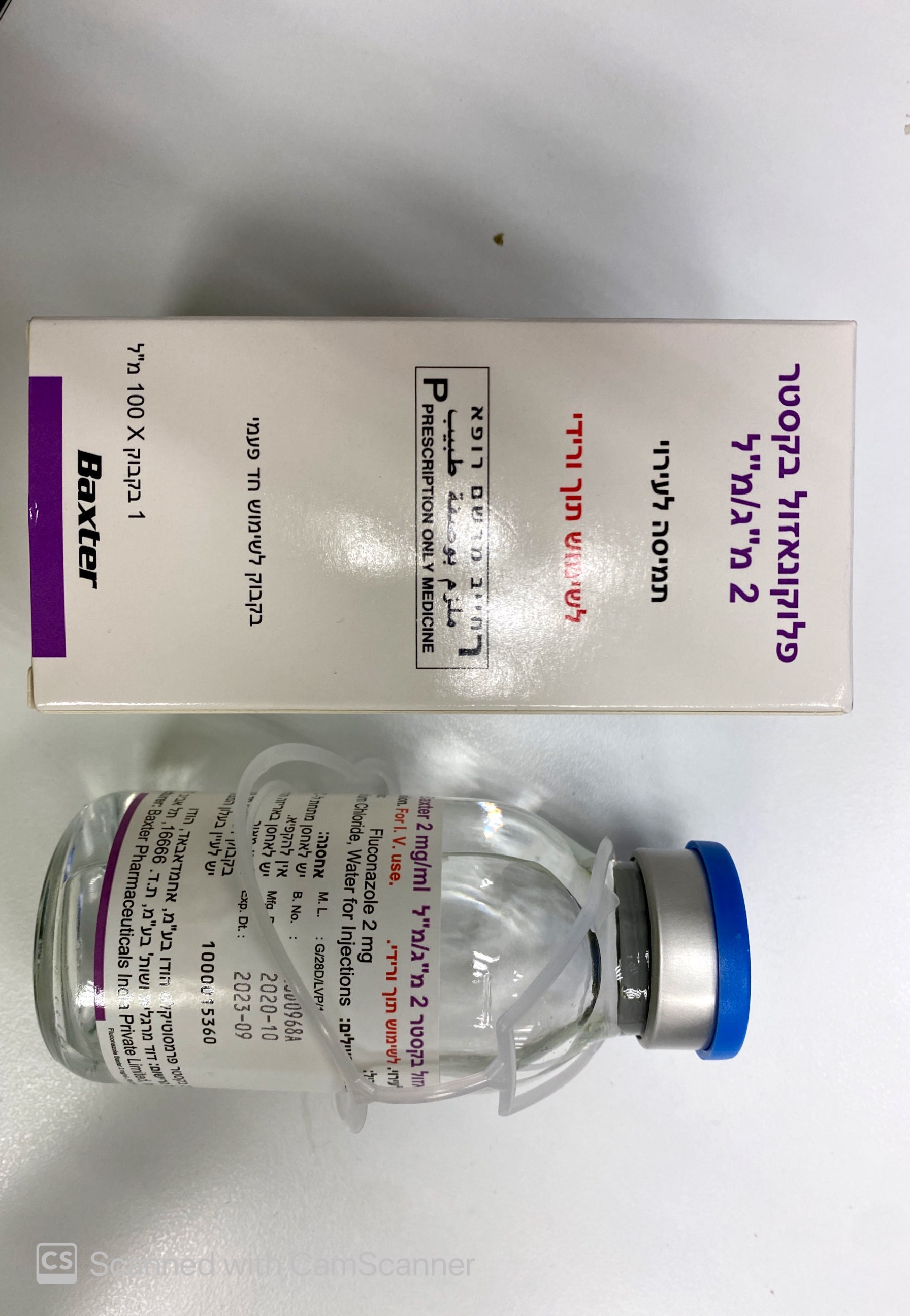
פלוקונאזול בקסטר 2 מ"ג/מ"ל FLUCONAZOLE BAXTER 2 MG/ML (FLUCONAZOLE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה לאינפוזיה : SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Posology : מינונים
4.2 Posology and method of administration prolongation of the QTc interval in patients receiving azole antifungals in conjunction with terfenadine, interaction studies have been performed. One study at a 200 mg daily dose of Posology fluconazole failed to demonstrate a prolongation in QTc interval. Another study at a 400 mg and 800 mg daily dose of fluconazole demonstrated that fluconazole taken in doses of 400 mg per day or The dose should be based on the nature and severity of the fungal infection. Treatment of infections greater significantly increases plasma levels of terfenadine when taken concomitantly. The requiring multiple dosing should be continued until clinical parameters or laboratory tests indicate combined use of fluconazole at doses of 400 mg or greater with terfenadine is contraindicated (see that active fungal infection has subsided. An inadequate period of treatment may lead to recurrence section 4.3). The coadministration of fluconazole at doses lower than 400 mg per day with of active infection. terfenadine should be carefully monitored. Adults Astemizole: Concomitant administration of fluconazole with astemizole may decrease the clearance of astemizole. Resulting increased plasma concentrations of astemizole can lead to QT Indications Posology Duration of treatment prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole and Cryptococcosis - Treatment of Loading dose: 400 mg Usually at least 6 to 8 astemizole is contraindicated (see section 4.3). cryptococcal meningitis on Day 1 weeks. In life Subsequent dose: 200 threatening infections Pimozide: Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of fluconazole with mg to 400 mg once the daily dose can be pimozide may result in inhibition of pimozide metabolism. Increased pimozide plasma daily increased to 800 mg concentrations can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes. - Maintenance therapy 200 mg once daily Indefinitely at a daily Coadministration of fluconazole and pimozide is contraindicated (see section 4.3). to prevent relapse of dose of 200 mg cryptococcal meningitis Quinidine: Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of fluconazole with in patients with high risk quinidine may result in inhibition of quinidine metabolism. Use of quinidine has been associated of recurrence. with QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole 200 mg to 400 mg once 11 months up to 24 and quinidine is contraindicated (see section 4.3). Coccidioidomycosis daily months or longer depending on the Erythromycin: Concomitant use of fluconazole and erythromycin has the potential to increase the patient. 800 mg daily risk of cardiotoxicity (prolonged QT interval, torsades de pointes) and consequently sudden heart may be considered for death. Coadministration of fluconazole and erythromycin is contraindicated (see section 4.3). some infections and especially for Concomitant use of the following other medicinal products cannot be recommended: meningeal disease Loading dose: 800 mg In general, the Halofantrine: Fluconazole can increase halofantrine plasma concentration due to an inhibitory Invasive candidiasis on Day 1 recommended duration effect on CYP3A4. Concomitant use of fluconazole and halofantrine has the potential to increase Subsequent dose: 400 of therapy for the risk of cardiotoxicity (prolonged QT interval, torsades de pointes) and consequently sudden mg once daily candidemia is for 2 heart death. This combination should be avoided (see section 4.4). weeks after first negative blood culture Concomitant use that should be used with caution: result and resolution of signs and symptoms Amiodarone: Concomitant administration of fluconazole with amiodarone may increase QT attributable to prolongation. Caution must be exercised if the concomitant use of fluconazole and amiodarone is candidemia. necessary, notably with high dose fluconazole (800 mg). - Oropharyngeal Loading dose: 200 mg 7 to 21 days (until candidiasis to 400 mg on Day 1 oropharyngeal Concomitant use of the following other medicinal products lead to precautions and dose Treatment of mucosal Subsequent dose: 100 candidiasis is in adjustments: candidiasis mg to 200 mg once remission). The effect of other medicinal products on fluconazole- daily Longer periods may be used in patients with Rifampicin: Concomitant administration of fluconazole and rifampicin resulted in a 25% decrease in severely compromised the AUC and a 20% shorter half-life of fluconazole. In patients receiving concomitant rifampicin, an immune function increase of the fluconazole dose should be considered. - Oesophageal Loading dose: 200 mg 14 to 30 days (until candidiasis to 400 mg on Day 1 oesophageal Interaction studies have shown that when oral fluconazole is coadministered with food, cimetidine, Subsequent dose: 100 candidiasis is in antacids or following total body irradiation for bone marrow transplantation, no clinically significant mg to 200 mg once remission). impairment of fluconazole absorption occurs. daily Longer periods may be used in patients with Hydrochlorothiazide: In a pharmacokinetic interaction study, coadministration of multiple-dose severely compromised hydrochlorothiazide to healthy volunteers receiving fluconazole increased plasma concentration of immune function fluconazole by 40%. An effect of this magnitude should not necessitate a change in the fluconazole - Candiduria 200 mg to 400 mg once 7 to 21 days. Longer dose regimen in subjects receiving concomitant diuretics. daily periods may be used in The effect of fluconazole on other medicinal products patients with severely compromised immune Fluconazole is a moderate inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes 2C9 and 3A4. function. Fluconazole is also a strong inhibitor of the isozyme CYP2C19. In addition to the - Chronic atrophic 50 mg once daily 14 days observed/documented interactions mentioned below, there is a risk of increased plasma candidiasis concentration of other compounds metabolized by CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 - Chronic 50 mg to 100 mg once Up to 28 days. Longer coadministered with fluconazole. Therefore caution should be exercised when using these mucocutaneous daily periods depending on combinations and the patients should be carefully monitored. The enzyme inhibiting effect of candidiasis both the severity of fluconazole persists 4-5 days after discontinuation of fluconazole treatment due to the long half-life infection or underlying of fluconazole (see section 4.3). immune compromisation and Alfentanil: During concomitant treatment with fluconazole (400 mg) and intravenous alfentanil (20 infection μg/kg) in healthy volunteers the alfentanil AUC 10 increased 2-fold, probably through inhibition of - Oropharyngeal 100 mg to 200 mg daily An indefinite period for CYP3A4. candidiasis or 200 mg 3 times per patients with chronic week. immune suppression Dose adjustment of alfentanil may be necessary. - Oesophageal 100 mg to 200 mg daily An indefinite period for Prevention of relapse candidiasis or 200 mg 3 times per patients with chronic Amitriptyline, nortriptyline: Fluconazole increases the effect of amitriptyline and nortriptyline. 5- of mucosal week immune suppression nortriptyline and/or S-amitriptyline may be measured at initiation of the combination therapy and candidiasis in after one week. Dose of amitriptyline/nortriptyline should be adjusted, if necessary. patients infected with HIV who are at high Amphotericin B: Concurrent administration of fluconazole and amphotericin B in infected normal risk of experiencing and immunosuppressed mice showed the following results: a small additive antifungal effect in relapse systemic infection with C. albicans, no interaction in intracranial infection with Cryptococcus Prophylaxis of 200 mg to 400 mg once Treatment should start neoformans, and antagonism of the two medicinal products in systemic infection with Aspergillus candidal infections daily several days before the fumigatus. The clinical significance of results obtained in these studies is unknown. anticipated onset of neutropenia and Anticoagulants: In post-marketing experience, as with other azole antifungals, bleeding events continue for 7 days (bruising, epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding, hematuria, and melena) have been reported, in after recovery from association with increases in prothrombin time in patients receiving fluconazole concurrently with neutropenia after the warfarin. During concomitant treatment with fluconazole and warfarin the prothrombin time was neutrophil count rises prolonged up to 2-fold, probably due to an inhibition of the warfarin metabolism through CYP2C9. above 1000 cells per In patients receiving coumarin-type or indanedione anticoagulants concurrently with fluconazole 3 mm . the prothrombin time should be carefully monitored. Dose adjustment of the anticoagulant may be necessary. Special populations Benzodiazepines (short acting), i.e. midazolam, triazolam: Following oral administration of Elderly midazolam, fluconazole resulted in substantial increases in midazolam concentrations and Dosage should be adjusted based on the renal function (see “Renal impairment”). psychomotor effects. Concomitant intake of fluconazole 200 mg and midazolam 7.5 mg orally increased the midazolam AUC and half-life 3.7-fold and 2.2-fold, respectively. Fluconazole 200 mg Renal impairment daily given concurrently with triazolam 0.25 mg orally increased the triazolam AUC and half-life 4.4- fold and 2.3-fold, respectively. Potentiated and prolonged effects of triazolam have been observed Fluconazole is predominantly excreted in the urine as unchanged active substance. No at concomitant treatment with fluconazole. If concomitant benzodiazepine therapy is necessary in adjustments in single dose therapy are necessary. In patients (including paediatric population) with patients being treated with fluconazole, consideration should be given to decreasing the impaired renal function who will receive multiple doses of fluconazole, an initial dose of 50 mg to benzodiazepine dose, and the patients should be appropriately monitored. 400 mg should be given, based on the recommended daily dose for the indication. After this initial loading dose, the daily dose (according to indication) should be based on the following table: Carbamazepine: Fluconazole inhibits the metabolism of carbamazepine and an increase in serum Creatinine clearance (ml/min) Percent of recommended dose carbamazepine of 30% has been observed. There is a risk of developing carbamazepine toxicity. >50 100 % Dose adjustment of carbamazepine may be necessary depending on concentration ≤ 50(no haemodialysis) 50 % measurements/effect. Haemodialysis 100% after each haemodialysis Calcium channel blockers: Certain calcium channel antagonists (nifedipine, isradipine, amlodipine, Patients on haemodialysis should receive 100% of the recommended dose after each verapamil and felodipine) are metabolized by CYP3A4. Fluconazole has the potential to increase haemodialysis; on non-dialysis days, patients should receive a reduced dose according to their the systemic exposure of the calcium channel antagonists. Frequent monitoring for adverse events creatinine clearance. is recommended. Hepatic impairment Celecoxib: During concomitant treatment with fluconazole (200 mg daily) and celecoxib (200 mg) the celecoxib Cmax and AUC increased by 68% and 134%, respectively. Half of the celecoxib dose Limited data are available in patients with hepatic impairment, therefore fluconazole should be may be necessary when combined with fluconazole. administered with caution to patients with liver dysfunction (see sections 4.4 and 4.8). Cyclophosphamide: Combination therapy with cyclophosphamide and fluconazole results in an Paediatric population increase in serum bilirubin and serum creatinine. The combination may be used while taking increased consideration to the risk of increased serum bilirubin and serum creatinine. A maximum dose of 400 mg daily should not be exceeded in paediatric population. Date: 31/03/21 Baxter Pharmaceuticals India Private Limited Fentanyl: One fatal case of fentanyl intoxication due to possible fentanyl fluconazole interaction As with similar infections in adults, the duration of treatment is based on the clinical and was reported. Furthermore, it was shown in healthy volunteers that fluconazole delayed the mycological response. Fluconazole is administered as a single daily dose. elimination of fentanyl significantly. Elevated fentanyl concentration may lead to respiratory depression. Patients should be monitored closely for the potential risk of respiratory depression. For paediatric patients with impaired renal function, see dosing in “Renal impairment”. The Dosage adjustment of fentanyl may be necessary. pharmacokinetics of fluconazole has not been studied in paediatric population with renal insufficiency (for “Term newborn infants” who often exhibit primarily renal immaturity please see HMG CoA reductase inhibitors: The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis increases when below). fluconazole is coadministered with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors metabolised through CYP3A4, Pantone such as atorvastatin and simvastatin, or through CYP2C9, such as fluvastatin. If concomitant Infants, toddlers and children (from 28 days to 11 years old): therapy is necessary, the patient should be observed for symptoms of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis and creatine kinase should be monitored. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors should Indication Posology Recommendations be discontinued if a marked increase in creatine kinase is observed or myopathy/rhabdomyolysis is - Mucosal candidiasis Initial dose: 6 mg/kg Initial dose may be used on the diagnosed or suspected. Subsequent dose: 3 mg/kg once first day to achieve steady state daily levels more rapidly Ibrutinib: Moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as fluconazole increase plasma ibrutinib - Invasive candidiasis Dose: 6 to 12 mg/kg once daily Depending on the severity of the concentrations and may increase risk of toxicity. If the combination cannot be avoided, reduce the - Cryptococcal meningitis disease dose of ibrutinib to 280 mg once daily (two capsules) for the duration of the inhibitor use and provide - Maintenance therapy to prevent Dose: 6 mg/kg once daily Depending on the severity of the close clinical monitoring. relapse of cryptococcal disease Ivacaftor: Co-administration with ivacaftor, a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (5) meningitis in children with high (CFTR) potentiator, increased ivacaftor exposure by 3-fold and hydroxymethyl-ivacaftor (M1) risk of recurrence exposure by 1.9-fold. A reduction of the ivacaftor dose to 150 mg once daily is recommended for Pantone - Prophylaxis of Candida in Dose: 3 to 12 mg/kg once daily Depending on the extent and patients taking concomitant moderate CYP3A inhibitors, such as fluconazole and erythromycin. immunocompromised patients duration of the induced neutropenia (see Adults Olaparib: Moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 such as fluconazole increase olaparib plasma posology) concentrations; concomitant use is not recommended. If the combination cannot be avoided, limit Adolescents (from 12 to 17 years old): the dose of olaparib to 200 mg twice daily. Size of Artwork (In mm) : 600x175 Depending on the weight and pubertal development, the prescriber would need to assess which Immunosuppresors (i.e. ciclosporin, everolimus, sirolimus and tacrolimus): posology (adults or children) is the most appropriate. Clinical data indicate that children have a Ciclosporin: Fluconazole significantly increases the concentration and AUC of ciclosporin. During higher fluconazole clearance than observed for adults. A dose of 100, 200 and 400 mg in adults concomitant treatment with fluconazole 200 mg daily and ciclosporin (2.7 mg/kg/day) there was a corresponds to a 3, 6 and 12 mg/kg dose in children to obtain a comparable systemic exposure. 1.8-fold increase in ciclosporin AUC. This combination may be used by reducing the dose of GSM of Paper/Board : 60 GSM ciclosporin depending on ciclosporin concentration. Term newborn infants (0 to 27 days): Neonates excrete fluconazole slowly. Everolimus: Although not studied in vivo or in vitro, fluconazole may increase serum concentrations Pantone Plant Location : Injectable of everolimus through inhibition of CYP3A4. Artwork Control Key No.: There are few pharmacokinetic data to support this posology in term newborn infants (see section Artwork Req. No: 27737 5.2). Sirolimus: Fluconazole increases plasma concentrations of sirolimus presumably by inhibiting the metabolism of sirolimus via CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein. This combination may be used with a Age group Posology Recommendations dose adjustment of sirolimus depending on the effect/concentration measurements. (4) Term newborn infants The same mg/kg dose as for A maximum dose of 12 mg/kg (0 to 14 days) infants, toddlers and children every 72 hours should not be Tacrolimus: Fluconazole may increase the serum concentrations of orally administered tacrolimus Language : English should be given every 72 hours exceeded up to 5 times due to inhibition of tacrolimus metabolism through CYP3A4 in the intestines. No Term newborn infants The same mg/kg dose as for A maximum dose of 12 mg/kg significant pharmacokinetic changes have been observed when tacrolimus is given intravenously. (from 15 to 27 days) infants, toddlers and children every 48 hours should not be Increased tacrolimus levels have been associated with nephrotoxicity. Dose of orally administered should be given every 48 hours exceeded tacrolimus should be decreased depending on tacrolimus concentration. Method of administration Losartan: Fluconazole inhibits the metabolism of losartan to its active metabolite (E-31 74) which is Pantone Fluconazole Baxter 2 mg/ml may be administered either orally or by intravenous infusion(solution responsible for most of the angiotensin II-receptor antagonism which occurs during treatment with for infusion), the route being dependent on the clinical state of the patient. On transferring from the losartan. Patients should have their blood pressure monitored continuously. intravenous to the oral route, or vice versa, there is no need to change the daily dose. Methadone: Fluconazole may enhance the serum concentration of methadone. Dose adjustment Intravenous infusion should be administrated at a rate not exceeding 10 ml/minute. Fluconazole of methadone may be necessary. Baxter 2 mg/ml is formulated in sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for infusion, each 200 mg (100 ml bottle) containing 15 mmol each of Na+ and C1-. Because Fluconazole Baxter 2 mg/ml is Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: The Cmax and AUC of flurbiprofen was increased by 23% and available as a dilute sodium chloride solution, in patients requiring sodium or fluid restriction, 81%, respectively, when coadministered with fluconazole compared to administration of consideration should be given to the rate of fluid administration. flurbiprofen alone. Similarly, the Cmax and AUC of the pharmacologically active isomer [S-(+)- ibuprofen] was increased by 15% and 82%, respectively, when fluconazole was coadministered (3) For instruction on dilution of the medicinal product before administration, see section 6.6. with racemic ibuprofen (400 mg) compared to administration of racemic ibuprofen alone. Although not specifically studied, fluconazole has the potential to increase the systemic exposure Pantone

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן: 1. לטיפול בחולה הסובל מקריפטוקוקוזיס, כולל דלקת קרום מוח קריפטוקוקאלית. 2. לטיפול בחולה הסובל מקנדידיאזיס מוקוזאלית. 3. לחולה העובר השתלת מוח עצם, או מטופל בכימותרפיה ציטוטוקסית או מטופל בהקרנות - לצורך טיפולי או מניעתי של קנדידיאזיס.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| לחולה העובר השתלת מוח עצם, או מטופל בכימותרפיה ציטוטוקסית או מטופל בהקרנות - לצורך טיפולי או מניעתי של קנדידיאזיס. | 01/03/2002 | |||
| לטיפול בחולה הסובל מקנדידיאזיס מוקוזאלית. | 01/03/2002 | |||
| לטיפול בחולה הסובל מקריפטוקוקוזיס, כולל דלקת קרום מוח קריפטוקוקאלית | 01/03/2002 |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis, cryptococcal meningitis
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
01/01/1995
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לרופא
11.07.21 - עלון לרופאעלון מידע לצרכן
לתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
פלוקונאזול בקסטר 2 מ"ג/מ"ל