Quest for the right Drug
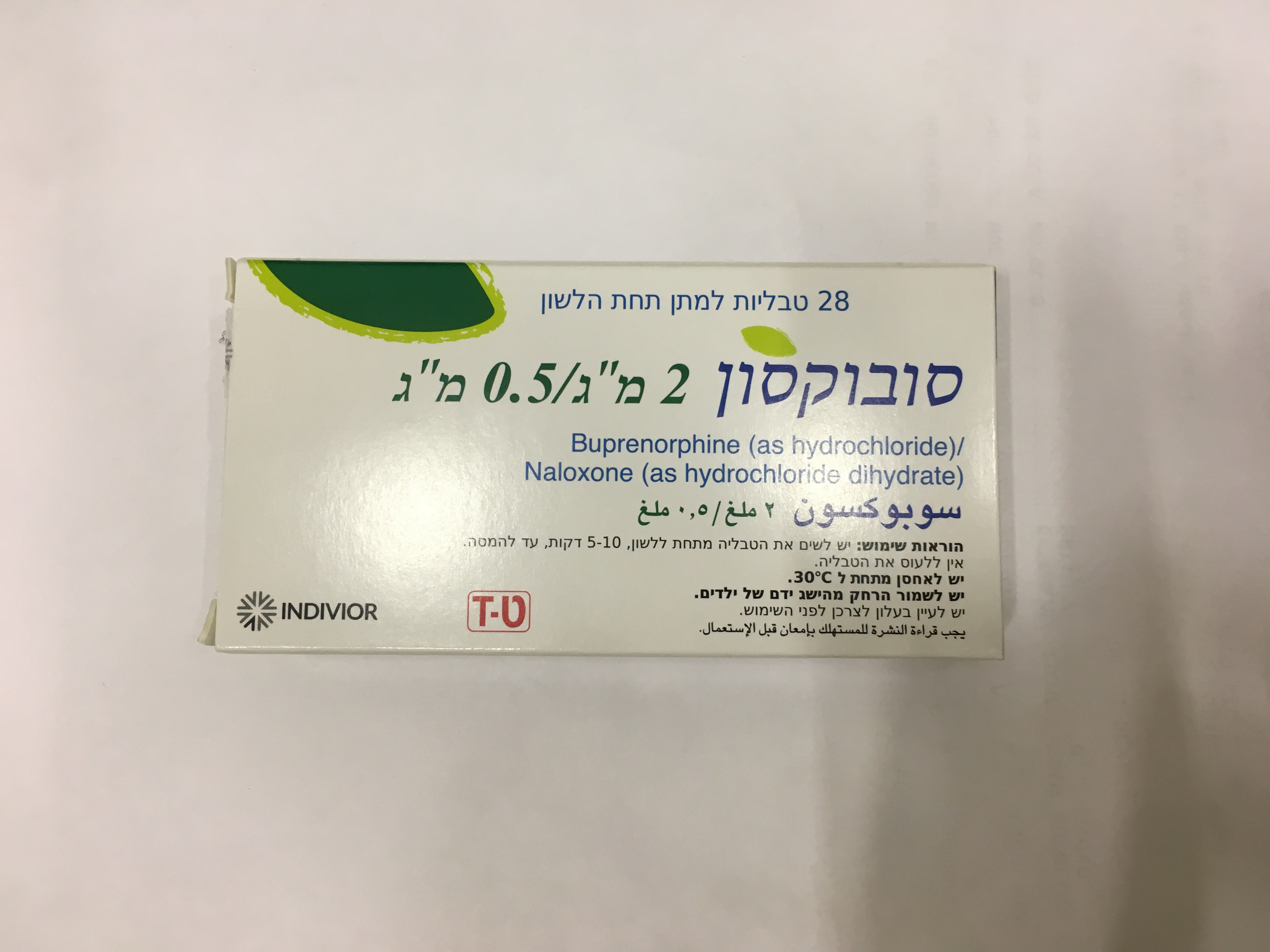
סובוקסון 2 מ"ג/ 0.5 מ"ג SUBOXONE 2 MG/0.5 MG (BUPRENORPHINE HYDROCHLORIDE, NALOXONE HYDROCHLORIDE DIHYDRATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
טבליות למתן מתחת ללשון : TABLETS SUBLINGUAL
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Interactions : אינטראקציות
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Buprenorphine/naloxone should not be taken together with: • Alcoholic drinks or medicinal products containing alcohol, as alcohol increases the sedative effect of buprenorphine (see section 4.7). Suboxone should be used cautiously when co-administered with: • Sedatives such as benzodiazepines or related medicinal products The concomitant use of opioids with sedative medicinal products such as benzodiazepines or related medicinal products increases the risk of sedation, respiratory depression, coma and death because of additive CNS depressant effect. The dose and duration of concomitant use of sedative medicinal products should be limited (see section 4.4). Patients should be warned that it is extremely dangerous to self-administer non-prescribed benzodiazepines while taking this product, and should also be cautioned to use benzodiazepines concurrently with this product only as directed by their physician (see section 4.4). • Other central nervous system depressants, other opioid derivatives (e.g. methadone, analgesics and antitussives), certain antidepressants, sedative H1-receptor antagonists, barbiturates, anxiolytics other than benzodiazepines, neuroleptics, clonidine and related substances: these combinations increase central nervous system depression. The reduced level of alertness can make driving and using machines hazardous. • Furthermore, adequate analgesia may be difficult to achieve when administering a full opioid agonist in patients receiving buprenorphine/naloxone. Therefore the potential to overdose with a full agonist exists, especially when attempting to overcome buprenorphine partial agonist effects, or when buprenorphine plasma levels are declining. • Serotonergic medicinal products, such as MAO inhibitors, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine re-uptake inhibitor (SNRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants as the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, is increased (see section 4.4). • Naltrexone and nalmefene are opioid antagonists that can block the pharmacological effects of buprenorphine. Co-administration during buprenorphine/naloxone treatment is contraindicated due to the potentially dangerous interaction that may precipitate a sudden onset of prolonged and intense opioid withdrawal symptoms (see section 4.3). • CYP3A4 inhibitors: an interaction study of buprenorphine with ketoconazole (a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4) resulted in increased Cmax and AUC (area under the curve) of buprenorphine (approximately 50 % and 70 % respectively) and, to a lesser extent, of norbuprenorphine. Patients receiving Suboxone should be closely monitored, and may require dose-reduction if combined with potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g. protease inhibitors like ritonavir, nelfinavir or indinavir or azole antifungals such as ketoconazole or itraconazole, macrolide antibiotics. • CYP3A4 inducers: Concomitant use of CYP3A4 inducers with buprenorphine may decrease buprenorphine plasma concentrations, potentially resulting in sub-optimal treatment of opioid dependence with buprenorphine. It is recommended that patients receiving buprenorphine/naloxone should be closely monitored if inducers (e.g. phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin, rifampicin) are co-administered. The dose of buprenorphine or the CYP3A4 inducer may need to be adjusted accordingly. • The concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) might produce exaggeration of the effects of opioids, based on experience with morphine.

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
09/01/2013
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
