Quest for the right Drug
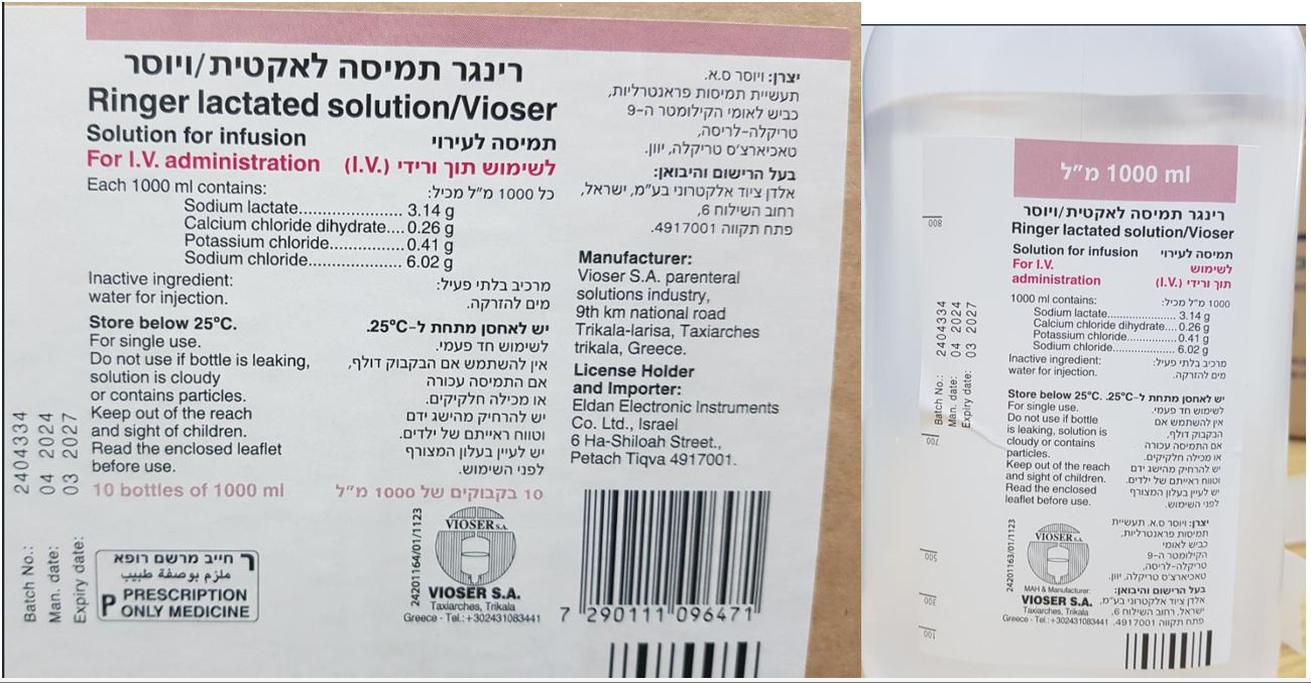
רינגר תמיסה לאקטית / ויוסר RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION/VIOSER (CALCIUM CHLORIDE DIHYDRATE, POTASSIUM CHLORIDE, SODIUM CHLORIDE, SODIUM LACTATE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תוך-ורידי : I.V
צורת מינון:
תמיסה לאינפוזיה : SOLUTION FOR INFUSION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4. Special warnings and precautions for use Hypersensitivity reactions The infusion must be stopped immediately if any signs or symptoms of a suspected hypersensitivity reaction develop. Appropriate therapeutic countermeasures must be instituted as clinically indicated. Incompatibilities Ceftriaxone In patients older than 28 days (including adults), ceftriaxone must not be administered simultaneously with intravenous calcium-containing solutions, including RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION, through the same infusion line. If the same infusion line is used for sequential administration, the line must be thoroughly flushed between infusions with a compatible fluid. For patients under 28 days please see section 4.3. Electrolyte balance Hypernatraemia RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should only be administered to patients with hypernatraemia after careful consideration of the underlying cause and alternative intravenous fluids. Monitoringof plasma sodium and volume status during treatment is recommended. RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution in patients with conditions predisposing to hypernatraemia (such as adrenocortical insufficiency, diabetes insipidus or extensive tissue injury) and in patients with cardiac disease. Hyperchloraemia RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should only be administered to patients with hyperchloraemia after careful consideration of the underlying cause and alternative intravenous fluids. Monitoring of plasma chloride and acid-base balance during treatment is recommended. RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution to patients with conditions predisposing to hyperchloraemia (such as renal failure and renal tubular acidosis, diabetes insipidus), and patients with urinary diversion or patients taking certain diuretics (carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, e.g., acetazolamide) or steroids (androgens, estrogens, corticosteroids) and in patients with severe dehydration. Use in patients with potassium deficiency Although RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION has a potassium concentration similar to the concentration in plasma, it is insufficient to produce a useful effect in case of severe potassium insufficiency and therefore it should not be used for this purpose. Use in patients at risk for hyperkalaemia RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution to patients with conditions predisposing to hyperkalaemia (such as severe renal impairment or adrenocortical insufficiency, acute dehydration, or extensive tissue injury or burns) and in patients with cardiac disease. The plasma potassium level of the patient must be particularly closely monitored in patients at risk of hyperkalaemia. Use in patients at risk for hypercalcaemia Calcium chloride is irritant, therefore care should be taken to prevent extravasation during intravenous injection and intramuscular injection must be avoided. Solutions containing calcium salts should be used with caution in patients with conditions predisposing to hypercalcaemia, such as patients with renal impairment and granulomatous diseases associated with increased calcitriol synthesis such as sarcoidosis, calcium renal calculi or a history of such calculi. Fluid balance/renal function Use in patients with renal impairment RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution to patients with renal impairment. In such patients, administration of RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION may result in sodium and/or potassium retention. Risk of fluid and/or solute overload and electrolyte disturbances Depending on the volume and rate of infusion, intravenous administration of RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION can cause: • fluid and/or solute overload resulting in overhydration and, for example, congested states, including pulmonary congestion and oedema. • clinically relevant electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalance. Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations may be necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient or the rate of administration warrants such evaluation. High volume infusion must be used under specific monitoring in patients with cardiac or pulmonary failure and in patients with non-osmotic vasopressin release (including SIADH), due to the risk of hospital-acquired hyponatraemia (see below). Hyponatraemia Patients with non-osmotic vasopressin release (e.g. in acute illness, pain, post-operative stress, infections, burns, and CNS diseases), patients with heart, liver and kidney diseases and patients exposed to vasopressin agonists (see section 4.5) are at particular risk of acute hyponatraemia upon infusion of hypotonic fluids. Acute hyponatraemia can lead to acute hyponatraemic encephalopathy (cerebral oedema) characterized by headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy and vomiting. Patients with cerebral oedema are at particular risk of severe, irreversible and life-threatening brain injury. Children, women in the fertile age and patients with reduced cerebral compliance (e.g. meningitis, intracranial bleeding, cerebral contusion and brain oedema) are at particular risk of the severe and life-threatening brain swelling caused by acute hyponatraemia. Use in patients with hypervolaemia, overhydration or conditions causing sodium retention and oedema RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION solution should be administered with particular caution to hypervolaemic or overhydrated patients. Due to the sodium chloride content, RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution to patients with conditions that may cause sodium retention, fluid overload and oedema, such as patients with primary hyperaldosteronism, secondary hyperaldosteronism (associated with, e.g., hypertension, congestive heart failure, renal artery stenosis, or nephrosclerosis), or preeclampsia (see also Section 4.5). Acid-base balance Use in patients at risk for alkalosis RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION should be administered with particular caution to patients at risk for alkalosis. Because lactate is metabolized to bicarbonate, administration may result in, or worsen, metabolic alkalosis. Seizure may be precipitated by the alkalosis induced by lactate but this is uncommon. Other warnings Administration of citrate anticoagulated/preserved blood Due to the risk of coagulation precipitated by its calcium content, RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION must not be added to or administered simultaneously through the same tubing with citrateanticoagulated/preserved blood. Use in patients with type 2 diabetes Lactate is a substrate for gluconeogenesis. Therefore glucose levels should be carefully monitored in patients receiving RINGER LACTATED SOLUTION. Administration Adding other medication or using an incorrect administration technique might cause the appearance of fever reactions due to the possible introduction of pyrogens. In such case the infusion must be stopped immediately. For information on incompatibilities and preparation of the product with additives, please see sections 6.2 and 6.6. During long term parenteral treatment, a convenient nutritive supply must be given to the patient. This medicinal product contains 13.1 mmol (or 301.3 mg) sodium per 100 ml, equivalent to 15% of the WHOrecommended maximum daily intake of 2 g sodium for an adult. This medicine contains 0.55 mmol (or 21.5 mg) potassium per 100 ml. To be taken into consideration by patients with reduced kidney function or patients on a controlled potassium diet.
Effects on Driving

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
רישום
169 66 36052 00
מחיר
0 ₪
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לרופא
27.02.23 - עלון לרופאעלון מידע לצרכן
27.02.23 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
רינגר תמיסה לאקטית / ויוסר