Quest for the right Drug
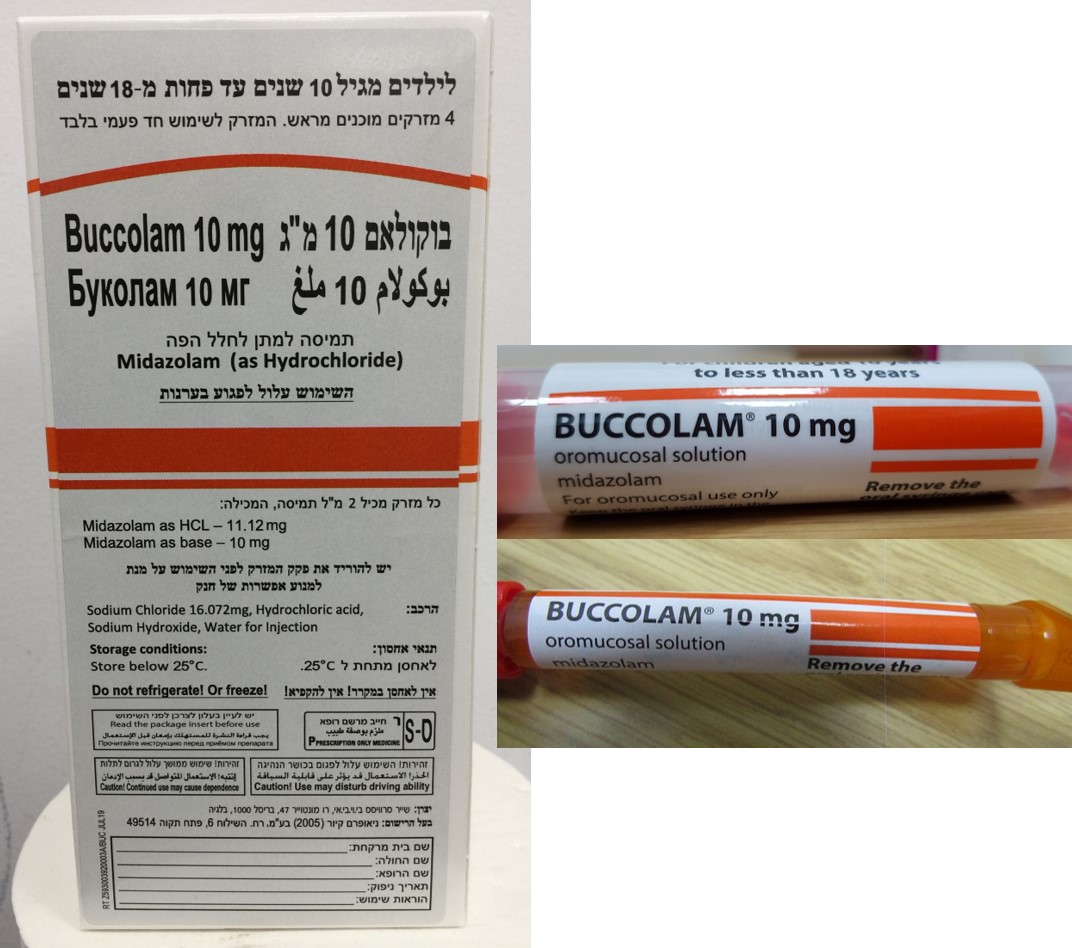
בוקולאם 10 מ"ג BUCCOLAM 10 MG (MIDAZOLAM AS HYDROCHLORIDE)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פנים הלחי : BUCCAL
צורת מינון:
תמיסה לחלל הפה : OROMUCOSAL SOLUTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Interactions : אינטראקציות
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Midazolam is metabolized by CYP3A4. Inhibitors and inducers of CYP3A4 have the potential to respectively increase and decrease the plasma concentrations and, subsequently, the effects of midazolam thus requiring dose adjustments accordingly. Pharmacokinetic interactions with CYP3A4 inhibitors or inducers are more pronounced for oral as compared to oromucosal or parenteral midazolam as CYP3A4 enzymes are also present in the upper gastro-intestinal tract. After oromucosal administration, only systemic clearance will be affected. After a single dose of oromucosal midazolam, the consequence on the maximal clinical effect due to CYP3A4 inhibition will be minor while the duration of effect may be prolonged. Hence, a careful monitoring of the clinical effects and vital signs is recommended during the use of midazolam with a CYP3A4 inhibitor even after a single dose. Anaesthetics and narcotic analgesics Fentanyl may reduce midazolam clearance. Antiepileptics Co-administration with midazolam may cause enhanced sedation or respiratory or cardiovascular depression. Midazolam may interact with other hepatically metabolised medicinal products, e.g. phenytoin, causing potentiation. Calcium-channel blockers Diltiazem and verapamil have been shown to reduce the clearance of midazolam and other benzodiazepines and may potentiate their actions. Ulcer-healing medicinal products Cimetidine, ranitidine and omeprazole have been shown to reduce the clearance of midazolam and other benzodiazepines and may potentiate their actions. Xanthines Metabolism of midazolam and other benzodiazepines is accelerated by xanthines. Dopaminergic medicinal products Midazolam may cause inhibition of levodopa. Muscle relaxants E.g. baclofen. Midazolam may cause potentiation of muscle relaxants, with increased CNS depressant effects. Nabilone Co-administration with midazolam may cause enhanced sedation or respiratory and cardiovascular depression. Medicinal products that inhibit CYP3A4 Medicinal product interactions following oromucosal administration of midazolam are likely to be similar to those observed after intravenous midazolam rather than oral administration. Food Grapefruit juice reduces the clearance of midazolam and potentiates its action. Azole antifungals Ketoconazole increased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by 5-fold while the terminal half-life increased by about 3-fold. Voriconazole increased the exposure of intravenous midazolam by 3-fold whereas its elimination half-life increased by about 3-fold. Fluconazole and itraconazole both increased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by 2 to 3- fold associated with an increase in terminal half-life by 2.4-fold for itraconazole and 1.5-fold for fluconazole. Posaconazole increased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by about 2-fold. Macrolide antibiotics Erythromycin resulted in an increase in the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by about 1.6 to 2 -fold associated with an increase of the terminal half-life of midazolam by 1.5 to 1.8-fold. Clarithromycin increased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by up to 2.5-fold associated with an increase in terminal half-life by 1.5 to 2-fold. HIV Protease inhibitors Co-administration with protease inhibitors (e.g. Saquinavir and other HIV protease inhibitors) may cause a large increase in the concentration of midazolam. Upon co-administration with ritonavir-boosted lopinavir, the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam increased by 5.4-fold, associated with a similar increase in terminal half-life. Calcium-channel blockers A single dose of diltiazem increased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by about 25% and the terminal half-life was prolonged by 43%. Various medicinal products Atorvastatin showed a 1.4-fold increase in plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam compared to control group. Medicinal products that induce CYP3A4 Rifampicin 7 days of 600 mg once daily decreased the plasma concentrations of intravenous midazolam by about 60%. The terminal half-life decreased by about 50-60%. Herbs St John’s Wort decreased plasma concentrations of midazolam by about 20-40% associated with a decrease in terminal half-life of about 15-17%. Depending on the specific St John's Wort extract, the CYP3A4-inducing effect may vary. Pharmacodynamic Drug-Drug Interactions (DDI) The co-administration of midazolam with other sedative/hypnotic medicinal products and CNS depressants, including alcohol, is likely to result in enhanced sedation and respiratory depression. Examples include opiate derivatives (used as analgesics, antitussives or substitutive treatments), antipsychotics, other benzodiazepines used as anxiolytics or hypnotics, barbiturates, propofol, ketamine, etomidate; sedative antidepressants, non-recent H1-antihistamines and centrally acting antihypertensive medicinal products. Alcohol, including alcohol-containing medicinal products may markedly enhance the sedative effect of midazolam. Alcohol intake should be strongly avoided in case of midazolam administration (see section 4.4). Midazolam decreases the minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of inhalation anaesthetics. The effect of CYP3A4 inhibitors may be larger in infants since part of the oromucosal dose is probably swallowed and absorbed in the gastro-intestinal tract.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול בהתקפי פרכוסים חריפים ממושכים בחולי אפילפסיה בגילאי 3 חודשים עד גיל 18 שנים.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| טיפול בהתקפי פרכוסים חריפים ממושכים בחולי אפילפסיה בגילאי 3 חודשים עד גיל 18 שנים. | ||||
| סטטוס אפילפטיקוס | ||||
| ATARALGESIA בשילוב עם קטאמין בילדים | ||||
| אינדוקציה ואחזקה של הרדמה | ||||
| סדציה בסיסית לפני התערבות אבחונית או כירורגית המבוצעת תחת הרדמה מקומית | ||||
| פרה-מדיקציה לפני אינדוקציה להרדמה |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
09/01/2013
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לרופא
03.04.24 - עלון לרופאעלון מידע לצרכן
12.10.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 08.03.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 08.03.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 02.04.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 02.04.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 19.09.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 19.09.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 19.09.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 15.08.17 - החמרה לעלון 14.07.19 - החמרה לעלון 12.01.21 - החמרה לעלון 13.04.22 - החמרה לעלון 12.10.22 - החמרה לעלון 03.04.24 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
בוקולאם 10 מ"ג