Quest for the right Drug
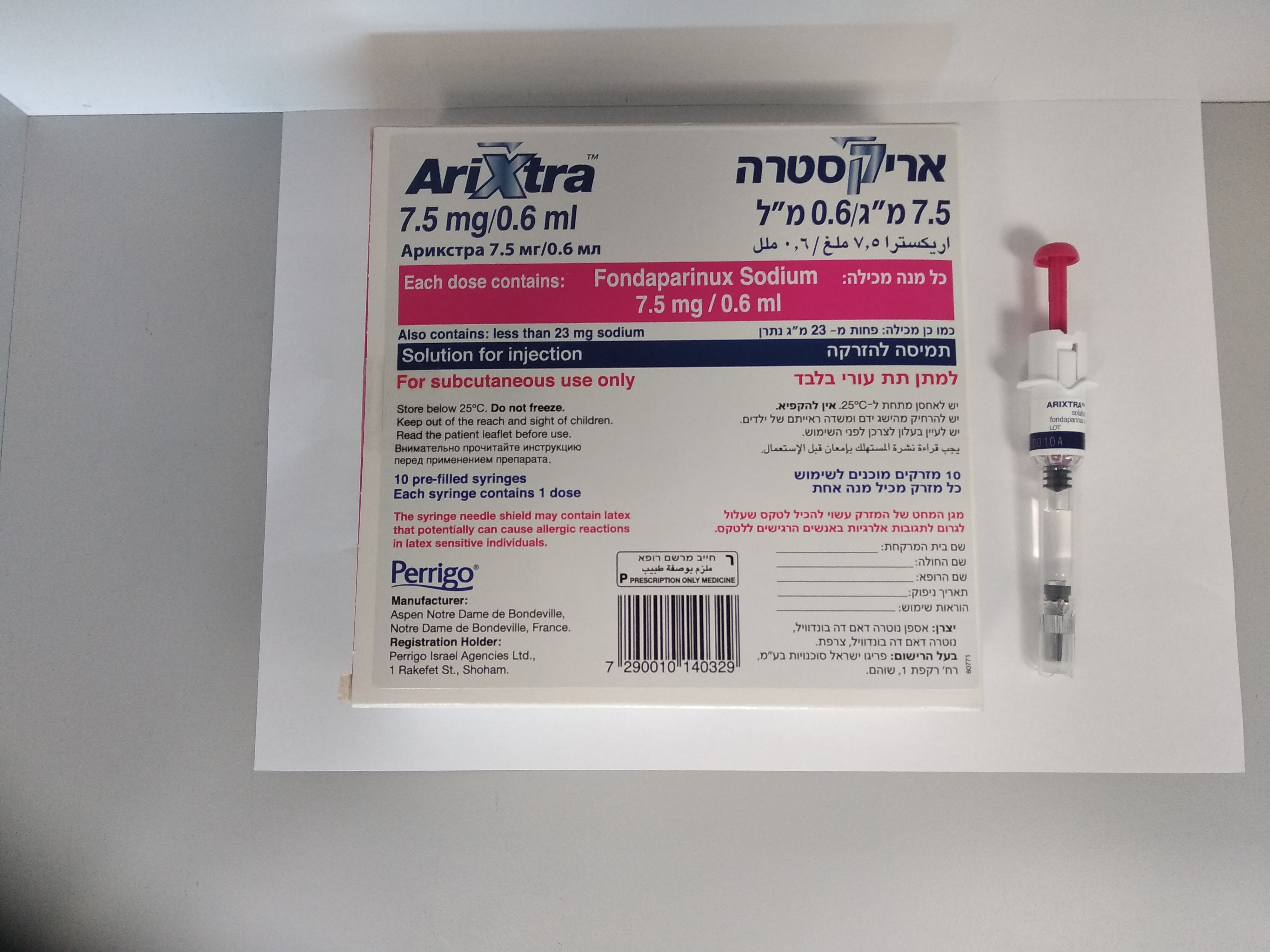
אריקסטרה 7.5 מ"ג / 0.6 מ"ל ARIXTRA 7.5 MG/0.6 ML (FONDAPARINUX SODIUM)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תת-עורי : S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Pharmacological properties : תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacodynamic Properties
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: antithrombotic agents. ATC code: B01AX05 Pharmacodynamic effects Fondaparinux is a synthetic and selective inhibitor of activated Factor X (Xa). The antithrombotic activity of fondaparinux is the result of antithrombin III (antithrombin) mediated selective inhibition of Factor Xa. By binding selectively to antithrombin, fondaparinux potentiates (about 300 times) the innate neutralization of Factor Xa by antithrombin. Neutralisation of Factor Xa interrupts the blood coagulation cascade and inhibits both thrombin formation and thrombus development. Fondaparinux does not inactivate thrombin (activated Factor II) and has no effects on platelets. At the doses used for treatment, fondaparinux does not, to a clinically relevant extent, affect routine coagulation tests such as activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), activated clotting time (ACT) or prothrombin time (PT)/International Normalised Ratio (INR) tests in plasma nor bleeding time or fibrinolytic activity. However, rare spontaneous reports of aPTT prolongation have been received. At higher doses, moderate changes in aPTT can occur. At the 10 mg dose used in interaction studies, fondaparinux did not significantly influence the anticoagulation activity (INR) of warfarin. Fondaparinux does not usually cross-react with sera from patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia (HIT). However, rare spontaneous reports of HIT in patients treated with fondaparinux have been received. Clinical studies The fondaparinux clinical program in treatment of Venous Thromboembolism was designed to demonstrate the efficacy of fondaparinux for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Over 4,874 patients were studied in controlled Phase II and III clinical studies. Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis In a randomised, double-blind, clinical trial in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of acute symptomatic DVT, fondaparinux 5 mg (body weight < 50 kg), 7.5 mg (body weight ≥ 50 kg, ≤ 100 kg) or 10 mg (body weight >100 kg) SC once daily was compared to enoxaparin sodium 1 mg/kg SC twice daily. A total of 2,192 patients were treated; for both groups, patients were treated for at least 5 days and up to 26 days (mean 7 days). Both treatment groups received Vitamin K antagonist therapy usually initiated within 72 hours after the first study drug administration and continued for 90 ± 7 days, with regular dose adjustments to achieve an INR of 2-3. The primary efficacy endpoint was the composite of confirmed symptomatic recurrent non-fatal VTE and fatal VTE reported up to Day 97. Treatment with fondaparinux was demonstrated to be non-inferior to enoxaparin (VTE rates 3.9% and 4.1%, respectively). Major bleeding during the initial treatment period was observed in 1.1% of fondaparinux patients, compared to 1.2% with enoxaparin. Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism A randomised, open-label, clinical trial was conducted in patients with acute symptomatic PE. The diagnosis was confirmed by objective testing (lung scan, pulmonary angiography or spiral CT scan). Patients who required thrombolysis or embolectomy or vena cava filter were excluded. Randomised patients could have been pre-treated with UFH during the screening phase but patients treated for more than 24 hours with therapeutic dose of anticoagulant or with uncontrolled hypertension were excluded. Fondaparinux 5 mg (body weight < 50 kg), 7.5 mg (body weight ≥ 50kg, ≤ 100 kg) or 10 mg (body weight >100 kg) SC once daily was compared to unfractionated heparin IV bolus (5,000 IU) followed by a continuous IV infusion adjusted to maintain 1.5–2.5 times aPTT control value. A total of 2,184 patients were treated; for both groups, patients were treated for at least 5 days and up to 22 days (mean 7 days). Both treatment groups received Vitamin K antagonist therapy usually initiated within 72 hours after the first study drug administration and continued for 90 ± 7 days, with regular dose adjustments to achieve an INR of 2-3. The primary efficacy endpoint was the composite of confirmed symptomatic recurrent non-fatal VTE and fatal VTE reported up to Day 97. Treatment with fondaparinux was demonstrated to be non-inferior to unfractionated heparin (VTE rates 3.8% and 5.0%, respectively). Major bleeding during the initial treatment period was observed in 1.3% of fondaparinux patients, compared to 1.1% with unfractionated heparin. A pilot dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of fondaparinux in children with deep vein thrombosis In an open-label study, 24 paediatric patients (n=10, age 1 to ≤ 5 years weight range 8-20 kg; n=7, age 6 to ≤ 12 years weight range 17-47 kg and n=7 age 13 to ≤ 18 years weight range 47-130 kg) diagnosed with venous thrombosis at study entry were administered fondaparinux. The majority of patients were Hispanic (67%) and 58% were male. Fondaparinux was administered at an initial dose of 0.1 mg/kg subcutaneously once daily and dosing was adjusted to achieve peak fondaparinux sodium concentrations of 0.5 to 1 mg/L after 4 hours. The median duration of treatment in this study was 3.5 days. The majority of patients (88%) achieved target fondaparinux concentrations at 4 hours after the first dose of fondaparinux. Two patients had reports of bleeding during the study. One experienced hypertensive encephalopathy accompanied by intracranial bleeding on day 5 of therapy resulting in fondaparinux discontinuation. Minor gastrointestinal bleeding was reported in another patient on day 5 of therapy which resulted in temporary discontinuation of fondaparinux. No conclusion can be drawn with regard to clinical efficacy in this uncontrolled study.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties The pharmacokinetics of fondaparinux sodium are derived from fondaparinux plasma concentrations quantified via anti factor Xa activity. Only fondaparinux can be used to calibrate the anti-Xa assay (the international standards of heparin or LMWH are not appropriate for this use). As a result, the concentration of fondaparinux is expressed as milligrams (mg). Absorption After subcutaneous dosing, fondaparinux is completely and rapidly absorbed (absolute bioavailability 100%). Following a single subcutaneous injection of fondaparinux 2.5 mg to young healthy subjects, peak plasma concentration (mean Cmax = 0.34 mg/l) is obtained 2 hours post-dosing. Plasma concentrations of half the mean Cmax values are reached 25 minutes post-dosing. In elderly healthy subjects, pharmacokinetics of fondaparinux is linear in the range of 2 to 8 mg by subcutaneous route. Following once daily dosing, steady state of plasma levels is obtained after 3 to 4 days with a 1.3-fold increase in Cmax and AUC. Mean (CV%) steady state pharmacokinetic parameters estimates of fondaparinux in patients undergoing hip replacement surgery receiving fondaparinux 2.5 mg once daily are: Cmax (mg/l) - 0.39 (31%), Tmax (h) - 2.8 (18%) and Cmin (mg/l) -0.14 (56%). In hip fracture patients, associated with their increased age, fondaparinux steady state plasma concentrations are: Cmax (mg/l) - 0.50 (32%), Cmin (mg/l) - 0.19 (58%). In DVT and PE treatment, patients receiving fondaparinux 5 mg (body weight <50 kg), 7.5 mg (body weight 50-100 kg inclusive) and 10 mg (body weight >100 kg) once daily, the body weight-adjusted doses provide similar exposure across all body weight categories. The mean (CV%) steady state pharmacokinetic parameters estimates of fondaparinux in patients with VTE receiving the fondaparinux proposed dose regimen once daily are: Cmax (mg/l) - 1.41 (23 %), Tmax (h) – 2.4 (8%) and Cmin (mg/l) -0.52 (45 %). The associated 5th and 95th percentiles are, respectively, 0.97 and 1.92 for Cmax (mg/l), and 0.24 and 0.95 for Cmin (mg/l). Distribution The distribution volume of fondaparinux is limited (7-11 litres). In vitro, fondaparinux is highly and specifically bound to antithrombin protein with a dose-dependant plasma concentration binding (98.6% to 97.0% in the concentration range from 0.5 to 2 mg/l). Fondaparinux does not bind significantly to other plasma proteins, including platelet factor 4 (PF4). Since fondaparinux does not bind significantly to plasma proteins other than antithrombin, no interaction with other medicinal products by protein binding displacement are expected. Biotransformation Although not fully evaluated, there is no evidence of fondaparinux metabolism and in particular no evidence for the formation of active metabolites. Fondaparinux does not inhibit CYP450s (CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A4) in vitro. Thus, fondaparinux is not expected to interact with other medicinal products in vivo by inhibition of CYP-mediated metabolism. Elimination The elimination half-life (t½) is about 17 hours in healthy young subjects and about 21 hours in healthy elderly subjects. Fondaparinux is excreted to 64 – 77 % by the kidney as unchanged compound. Special populations Paediatric patients - Limited data are available in paediatric patients (see section 5.1). Elderly patients - Renal function may decrease with age and thus, the elimination capacity for fondaparinux may be reduced in elderly. In patients >75 years undergoing orthopaedic surgery and receiving fondaparinux 2.5 mg once daily, the estimated plasma clearance was 1.2 to 1.4 times lower than in patients <65 years. A similar pattern is observed in DVT and PE treatment patients. Renal impairment - Compared with patients with normal renal function (creatinine clearance > 80 ml/min) undergoing orthopaedic surgery and receiving fondaparinux 2.5 mg once daily, plasma clearance is 1.2 to 1.4 times lower in patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50 to 80 ml/min) and on average 2 times lower in patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to 50 ml/min). In severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min), plasma clearance is approximately 5 times lower than in normal renal function. Associated terminal half-life values were 29 h in moderate and 72 h in patients with severe renal impairment. A similar pattern is observed in DVT and PE treatment patients. Body weight - Plasma clearance of fondaparinux increases with body weight (9% increase per 10 kg). Gender - No gender differences were observed after adjustment for body weight. Race - Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied prospectively. However, studies performed in Asian (Japanese) healthy subjects did not reveal a different pharmacokinetic profile compared to Caucasian healthy subjects. Similarly, no plasma clearance differences were observed between black and Caucasian patients undergoing orthopaedic surgery. Hepatic impairment - Following a single, subcutaneous dose of fondaparinux in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Category B), total (i.e., bound and unbound) Cmax and AUC were decreased by 22% and 39%, respectively, as compared to subjects with normal liver function. The lower plasma concentrations of fondaparinux were attributed to reduced binding to ATIII secondary to the lower ATIII plasma concentrations in subjects with hepatic impairment thereby resulting in increased renal clearance of fondaparinux. Consequently, unbound concentrations of fondaparinux are expected to be unchanged in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, and therefore, no dose adjustment is necessary based on pharmacokinetics. The pharmacokinetics of fondaparinux has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (see sections 4.2 and 4.4).

שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
לא צוין
הגבלות
לא צוין
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
09.07.19 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 17.04.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 09.07.19 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 03.01.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 03.01.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 03.01.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 07.11.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 15.01.12 - החמרה לעלון 11.08.13 - החמרה לעלון 01.11.18 - החמרה לעלון 07.11.24 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
אריקסטרה 7.5 מ"ג / 0.6 מ"ל