Quest for the right Drug
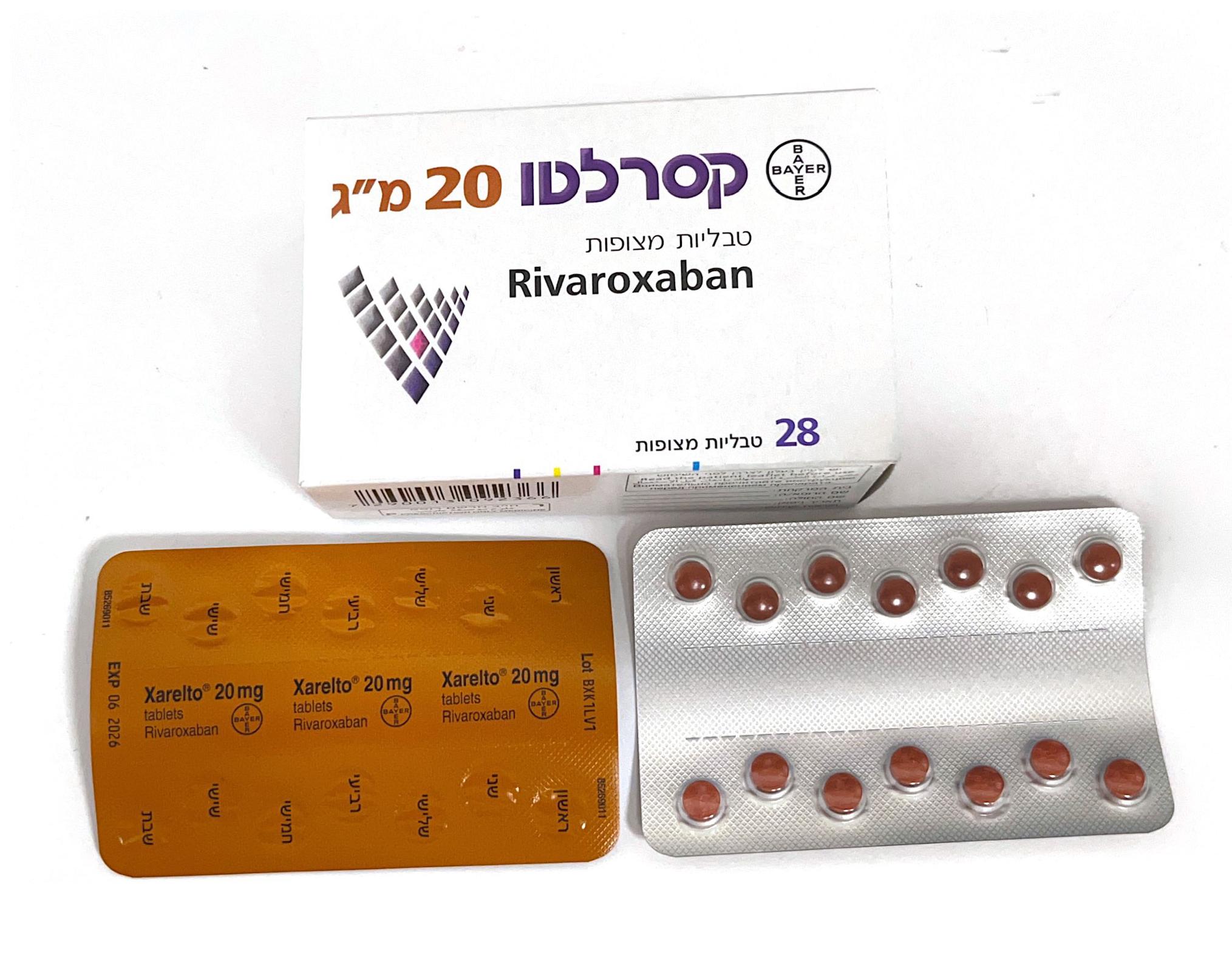
קסרלטו 20 מ"ג XARELTO 20 MG (RIVAROXABAN MICRONIZED)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
פומי : PER OS
צורת מינון:
טבליות מצופות פילם : FILM COATED TABLETS
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Clinical surveillance in line with anticoagulation practice is recommended throughout the treatment period. Haemorrhagic risk As with other anticoagulants, patients taking Xarelto are to be carefully observed for signs of bleeding. It is recommended to be used with caution in conditions with increased risk of haemorrhage. Xarelto administration should be discontinued if severe haemorrhage occurs (see section 4.9). In the clinical studies mucosal bleedings (i.e. epistaxis, gingival, gastrointestinal, genito urinary including abnormal vaginal or increased menstrual bleeding) and anaemia were seen more frequently during long term rivaroxaban treatment compared with VKA treatment. Thus, in addition to adequate clinical surveillance, laboratory testing of haemoglobin/haematocrit could be of value to detect occult bleeding and quantify the clinical relevance of overt bleeding, as judged to be appropriate. Several sub-groups of patients, as detailed below, are at increased risk of bleeding. These patients are to be carefully monitored for signs and symptoms of bleeding complications and anaemia after initiation of treatment (see section 4.8). Any unexplained fall in haemoglobin or blood pressure should lead to a search for a bleeding site. Although treatment with rivaroxaban does not require routine monitoring of exposure, rivaroxaban levels measured with a calibrated quantitative anti-factor Xa assay may be useful in exceptional situations where knowledge of rivaroxaban exposure may help to inform clinical decisions, e.g., overdose and emergency surgery (see sections 5.1 and 5.2). Paediatric population There is limited data in children with cerebral vein and sinus thrombosis who have a CNS infection (see section 5.1). The risk of bleeding should be carefully evaluated before and during therapy with rivaroxaban. Renal impairment In adult patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min) rivaroxaban plasma levels may be significantly increased (1.6 fold on average) which may lead to an increased bleeding risk. Xarelto is to be used with caution in patients with creatinine clearance 15 - 29 ml/min. Use is not recommended in patients with creatinine clearance < 15 ml/min (see sections 4.2 and 5.2). Xarelto should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment concomitantly receiving other medicinal products which increase rivaroxaban plasma concentrations (see section 4.5). Xarelto is not recommended in children and adolescents with moderate or severe renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2), as no clinical data is available. Interaction with other medicinal products The use of Xarelto is not recommended in patients receiving concomitant systemic treatment with azole-antimycotics (such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole and posaconazole) or HIV protease inhibitors (e.g. ritonavir). These active substances are strong inhibitors of both CYP3A4 and P-gp and therefore may increase rivaroxaban plasma concentrations to a clinically relevant degree (2.6 fold on average) which may lead to an increased bleeding risk. No clinical data is available in children receiving concomitant systemic treatment with strong inhibitors of both CYP3A4 and P-gp (see section 4.5). Care is to be taken if patients are treated concomitantly with medicinal products affecting haemostasis such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicinal products (NSAIDs), acetylsalicylic acid and platelet aggregation inhibitors or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). For patients at risk of ulcerative gastrointestinal disease an appropriate prophylactic treatment may be considered (see section 4.5). Other haemorrhagic risk factors As with other antithrombotics, rivaroxaban is not recommended in patients with an increased bleeding risk such as: • congenital or acquired bleeding disorders • uncontrolled severe arterial hypertension • other gastrointestinal disease without active ulceration that can potentially lead to bleeding complications (e.g. inflammatory bowel disease, oesophagitis, gastritis and gastroesophageal reflux disease). • vascular retinopathy • bronchiectasis or history of pulmonary bleeding. Patients with cancer Patients with malignant disease may simultaneously be at higher risk of bleeding and thrombosis. The individual benefit of antithrombotic treatment should be weighed against risk for bleeding in patients with active cancer dependent on tumour location, antineoplastic therapy and stage of disease. Tumours located in the gastrointestinal or genitourinary tract have been associated with an increased risk of bleeding during rivaroxaban therapy. In patients with malignant neoplasms at high risk of bleeding, the use of rivaroxaban is contraindicated (see section 4.3). Patients with prosthetic valves Rivaroxaban should not be used for thromboprophylaxis in patients having recently undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).Safety and efficacy of Xarelto have not been studied in patients with prosthetic heart valves; therefore, there are no data to support that Xarelto provides adequate anticoagulation in this patient population. Treatment with Xarelto is not recommended for these patients. Patients with antiphospholipid syndrome Direct acting Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) including rivaroxaban are not recommended for patients with a history of thrombosis who are diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome. In particular for patients that are triple positive (for lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, and anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibodies), treatment with DOACs could be associated with increased rates of recurrent thrombotic events compared with vitamin K antagonist therapy Haemodynamically unstable PE patients or patients who require thrombolysis or pulmonary embolectomy Xarelto is not recommended as an alternative to unfractionated heparin in patients with pulmonary embolism who are haemodynamically unstable or may receive thrombolysis or pulmonary embolectomy since the safety and efficacy of Xarelto have not been established in these clinical situations. Spinal/epidural anaesthesia or puncture When neuraxial anaesthesia (spinal/epidural anaesthesia) or spinal/epidural puncture is employed, patients treated with antithrombotic agents for prevention of thromboembolic complications are at risk of developing an epidural or spinal haematoma which can result in long-term or permanent paralysis [See boxed warning]. The risk of these events may be increased by the post-operative use of indwelling epidural catheters or the concomitant use of medicinal products affecting haemostasis. The risk may also be increased by traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal puncture. Patients are to be frequently monitored for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment (e.g. numbness or weakness of the legs, bowel or bladder dysfunction). If neurological compromise is noted, urgent diagnosis and treatment is necessary. Prior to neuraxial intervention the physician should consider the potential benefit versus the risk in anticoagulated patients or in patients to be anticoagulated for thromboprophylaxis. There is no clinical experience with the use of 20 mg rivaroxaban in these situations. To reduce the potential risk of bleeding associated with the concurrent use of rivaroxaban and neuraxial (epidural/spinal) anaesthesia or spinal puncture, consider the pharmacokinetic profile of rivaroxaban. Placement or removal of an epidural catheter or lumbar puncture is best performed when the anticoagulant effect of rivaroxaban is estimated to be low. However, the exact timing to reach a sufficiently low anticoagulant effect in each patient is not known and should be weighed against the urgency of a diagnostic procedure. For the removal of an epidural catheter and based on the general PK characteristics at least 2x half- life, i.e. at least 18 hours in young adult patients and 26 hours in elderly patients should elapse after the last administration of rivaroxaban (see section 5.2). Following removal of the catheter, at least 6 hours should elapse before the next rivaroxaban dose is administered. If traumatic puncture occurs the administration of rivaroxaban is to be delayed for 24 hours. No data is available on the timing of the placement or removal of neuraxial catheter in children while on Xarelto. In such cases, discontinue rivaroxaban and consider a short acting parenteral anticoagulant. Dosing recommendations before and after invasive procedures and surgical intervention If an invasive procedure or surgical intervention is required, Xarelto 20 mg should be stopped at least 24 hours before the intervention, if possible and based on the clinical judgement of the physician. If the procedure cannot be delayed the increased risk of bleeding should be assessed against the urgency of the intervention. Xarelto should be restarted as soon as possible after the invasive procedure or surgical intervention provided the clinical situation allows and adequate haemostasis has been established as determined by the treating physician (see section 5.2). Elderly population Increasing age may increase haemorrhagic risk (see section 5.2). Dermatological reactions Serious skin reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome/ toxic epidermal necrolysis and DRESS syndrome, have been reported during post-marketing surveillance in association with the use of rivaroxaban (see section 4.8). Patients appear to be at highest risk for these reactions early in the course of therapy: the onset of the reaction occurring in the majority of cases within the first weeks of treatment. Rivaroxaban should be discontinued at the first appearance of a severe skin rash (e.g. spreading, intense and/or blistering), or any other sign of hypersensitivity in conjunction with mucosal lesions. Information about excipients Xarelto contains lactose. Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, total lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicinal product. This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dosage unit, that is to say essentially “sodium-free”. Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events after Premature Discontinuation Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including Xarelto, in the absence of adequate alternative anticoagulation increases the risk of thrombotic events. An increased rate of stroke was observed during the transition from Xarelto to warfarin in clinical trials in atrial fibrillation patients. If Xarelto is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant [for conversion instructions see Dosage and Administration (4.2)]
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines Xarelto has minor influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Adverse reactions like syncope (frequency: uncommon) and dizziness (frequency: common) have been reported (see section 4.8). Patients experiencing these adverse reactions should not drive or use machines.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול במקרים האלה: א. מניעת תרומבואמבוליזם לאחר ניתוח להחלפת מפרק הירך. ב. מניעת תרומבואמבוליזם לאחר ניתוח להחלפת הברך. ג. מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות המטופלים ב-warfarin וחוו CVA או TIA עם ביטוי קליני (שטופל או אובחן בבית חולים) במהלך השנה האחרונה. ד. מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות המטופלים ב-Warfarin ושתועד אצלם INR גבוה מ-5 לפחות פעמיים במהלך השנה האחרונה באירועים נפרדים. ה. מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 Vasc score בערך 2 ומעלה.ו. טיפול קצר טווח למניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 score בערך 0 או 1 אחרי היפוך קצב ופעולות של אבלציות בפרפור.ז. טיפול ומניעה שניונית של פקקת הורידים העמוקים (Deep vein thrombosis – DVT).ח. טיפול ומניעה שניונית של תסחיף ריאתי (Pulmonary embolism - PE).ט. טיפול למניעת שבץ, אוטם שריר הלב, מוות קרדיווסקולרי, איסכמיה חריפה בגפיים ותמותה עבור חולים במחלת לב איסכמית ידועה (Ischemic heart disease (IHD) או Coronary artery disease (CAD)) ביחד עם מחלת כלי דם פריפרית (Peripheral arterial disease (PAD)).לעניין זה יוגדרו:1. מחלת לב איסכמית ידועה (IHD או CAD) - מצב לאחר אוטם או רה וסקולריזציה בעבר או היצרויות כליליות ידועות.2. מחלת כלי דם פריפרית (PAD) – א. מצב לאחר רה וסקולריזציה או ניתוח כלי דם או קטיעה בעבר, או קיום צליעה לסירוגין עם ABI מתחת ל-0.9 או היצרות כלי דם ידועה גדול מ-50% ב. מחלה בעורקי התרדמה (קרוטיד) מצב לאחר רה-וסקולריזציה או הצרות ידועה גדול מ-50%
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| טיפול למניעת שבץ, אוטם שריר הלב, מוות קרדיווסקולרי, איסכמיה חריפה בגפיים ותמותה עבור חולים במחלת לב איסכמית ידועה (Ischemic heart disease (IHD) או Coronary artery disease (CAD)) ביחד עם מחלת כלי דם פריפרית (Peripheral arterial disease (PAD)). | 16/01/2019 | המטולוגיה | ||
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 Vasc score בערך 2 ומעלה | 16/01/2019 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| טיפול ומניעה שניונית של תסחיף ריאתי (Pulmonary embolism - PE) | 11/01/2018 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| טיפול ומניעה שניונית של פקקת הורידים העמוקים (Deep vein thrombosis – DVT). | 11/01/2018 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| טיפול קצר טווח למניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 score בערך 0 או 1 אחרי היפוך קצב ופעולות של אבלציות בפרפור | 11/01/2018 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 score בערך 2 ומעלה | 21/01/2016 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 score בערך 3 ומעלה | 12/01/2014 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות בלא מחלה מסתמית ו-CHADS2 score בערך 4 ומעלה | 10/01/2012 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות המטופלים ב-Warfarin ושתועד אצלם INR גבוה מ-5 לפחות פעמיים במהלך השנה האחרונה באירועים נפרדים | 10/01/2012 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת שבץ ותסחיף סיסטמי בחולים עם פרפור עליות המטופלים ב-warfarin וחוו CVA או TIA עם ביטוי קליני (שטופל או אובחן בבית חולים) במהלך השנה האחרונה | 10/01/2012 | המטולוגיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת תרומבואמבוליזם לאחר ניתוח להחלפת הברך | 03/01/2010 | אורתופדיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN | |
| מניעת תרומבואמבוליזם לאחר ניתוח להחלפת מפרק הירך | 03/01/2010 | אורתופדיה | APIXABAN, DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE, RIVAROXABAN |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
03/01/2010
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
עלון מידע לצרכן
02.05.13 - עלון לצרכן 09.12.13 - עלון לצרכן 05.03.19 - עלון לצרכן 17.03.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.10.15 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 19.02.20 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 14.10.15 - עלון לצרכן עברית 17.03.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.10.15 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 04.08.20 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 18.10.21 - עלון לצרכן עברית 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן עברית 10.08.22 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 11.06.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 11.06.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 09.08.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 14.08.23 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 14.08.23 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 02.09.23 - עלון לצרכן עברית 29.02.24 - עלון לצרכן אנגלית 29.02.24 - עלון לצרכן עברית 29.02.24 - עלון לצרכן ערבית 14.05.14 - החמרה לעלון 02.05.16 - החמרה לעלון 30.01.20 - החמרה לעלון 06.07.21 - החמרה לעלון 18.10.21 - החמרה לעלון 02.05.13 - החמרה לעלון 16.03.23 - החמרה לעלון 11.06.23 - החמרה לעלון 11.06.23 - החמרה לעלוןלתרופה במאגר משרד הבריאות
קסרלטו 20 מ"ג