Quest for the right Drug
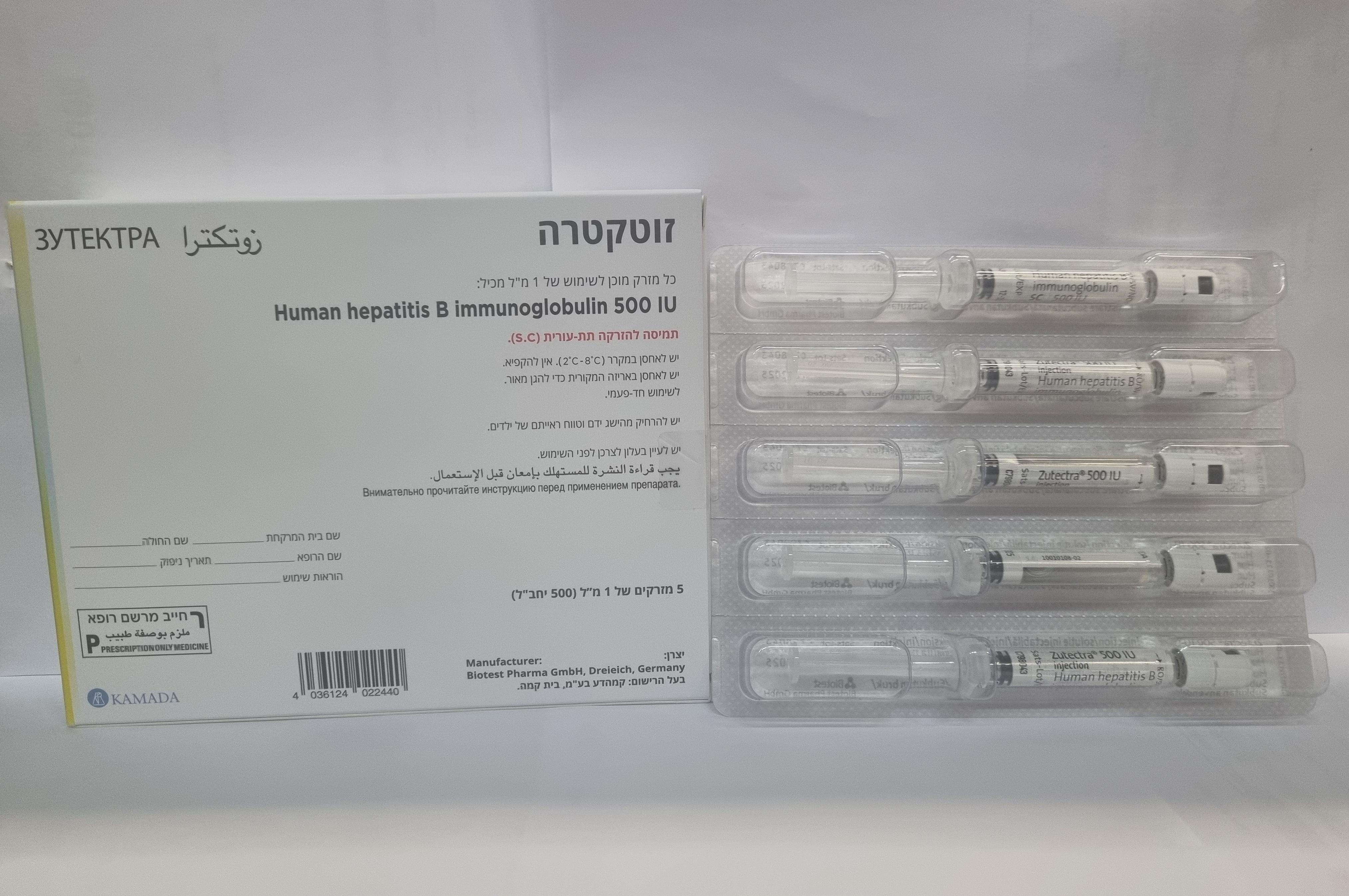
זוטקטרה ZUTECTRA (HUMAN HEPATITIS B IMMUNOGLOBULIN)
תרופה במרשם
תרופה בסל
נרקוטיקה
ציטוטוקסיקה
צורת מתן:
תת-עורי : S.C
צורת מינון:
תמיסה להזרקה : SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
עלון לרופא
מינוניםPosology התוויות
Indications תופעות לוואי
Adverse reactions התוויות נגד
Contraindications אינטראקציות
Interactions מינון יתר
Overdose הריון/הנקה
Pregnancy & Lactation אוכלוסיות מיוחדות
Special populations תכונות פרמקולוגיות
Pharmacological properties מידע רוקחי
Pharmaceutical particulars אזהרת שימוש
Special Warning עלון לרופא
Physicians Leaflet
Special Warning : אזהרת שימוש
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Traceability In order to improve the traceability of biological medicinal products, the name and the batch number of the administered product should be clearly recorded. This recommendation applies also for documentation in the treatment diary during self-administration of the medicinal product in a home treatment. Ensure that Zutectra is not administered into a blood vessel, because of the risk of shock. If the recipient is a carrier of HBsAg, there is no benefit in administering this medicinal product. There is no data about efficacy in post-exposure prophylaxis. Hypersensitivity True hypersensitivity reactions are rare. Zutectra contains a small quantity of IgA (see section 2). Individuals who are deficient in IgA have the potential for developing IgA antibodies and may have anaphylactic reactions after administration of blood components containing IgA. The physician must therefore weigh the benefit of treatment with Zutectra against the potential risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Rarely, human hepatitis B immunoglobulin can induce a fall in blood pressure with anaphylactic reaction, even in patients who have tolerated previous treatment with human immunoglobulin. Potential complications can often be avoided by ensuring that patients: - are not sensitive to human normal immunoglobulin, by initially injecting the product slowly; - are carefully monitored for any symptoms throughout the injection. In particular, patients naive to human normal immunoglobulin, patients switched from an alternative product or when there has been a long interval since the previous injection should be monitored during the first injection and for the first hour after the first injection, in order to detect potential adverse signs. All other patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes after administration. Suspicion of allergic or anaphylactic type reactions requires immediate discontinuation of the injection. In case of shock, standard medical treatment for shock should be implemented. Interference with serological testing After injection of immunoglobulin the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may result in misleading positive results in serological testing. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens, e.g. A, B, D may interfere with some serological tests for red cell antibodies, for example the direct antiglobulin test (DAT, direct Coombs’ test). Transmissible agents Standard measures to prevent infections resulting from the use of medicinal products prepared from human blood or plasma include selection of donors, screening of individual donations and plasma pools for specific markers of infection and the inclusion of effective manufacturing steps for the inactivation/removal of viruses. Despite this, when medicinal products prepared from human blood or plasma are administered, the possibility of transmitting infective agents cannot be totally excluded. This also applies to unknown or emerging viruses and other pathogens. The measures taken are considered effective for enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), and for the non-enveloped hepatitis A virus (HAV). The measures taken may be of limited value against non-enveloped viruses such as parvovirus B19. There is reassuring clinical experience regarding the lack of hepatitis A or parvovirus B19 transmission with immunoglobulins and it is also assumed that the antibody content makes an important contribution to the viral safety.
Effects on Driving
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines Hepatitis B immunoglobulin has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.

פרטי מסגרת הכללה בסל
התרופה תינתן לטיפול בכל אחד מאלה: א. מניעה לאחר חשיפה לוירוס HBV. ב. ילודים לאמהות נשאיות HBV. ג. חיסון פסיבי למניעת זיהום חוזר ב-HBV לאחר השתלת כבד.
מסגרת הכללה בסל
התוויות הכלולות במסגרת הסל
| התוויה | תאריך הכללה | תחום קליני | Class Effect | מצב מחלה |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| חיסון פסיבי למניעת זיהום חוזר ב-HBV לאחר השתלת כבד. | ||||
| ילודים לאמהות נשאיות HBV. | ||||
| מניעה לאחר חשיפה לוירוס HBV. |
שימוש לפי פנקס קופ''ח כללית 1994
לא צוין
תאריך הכללה מקורי בסל
15/04/2005
הגבלות
תרופה מוגבלת לרישום ע'י רופא מומחה או הגבלה אחרת
מידע נוסף
